HIPRT-Path-Tracer
HIPRT & Orochi Monte Carlo Path Tracer
Overview
Physically based Monte Carlo path tracer written with the HIPRT and Orochi libraries.
HIPRT is AMD’s equivalent to OptiX. It allows the use of the ray tracing accelerators of RDNA2+ AMD GPUs and can run on NVIDIA devices as well (although it wouldn’t take advatange of RT cores) as it is not AMD specific.
The Orochi library allows the loading of HIP and CUDA libraries at runtime meaning that the application doesn’t have to be recompiled to be used on a GPU from a different vendor (unlike HIP which would require a recompilation + linking).
Features
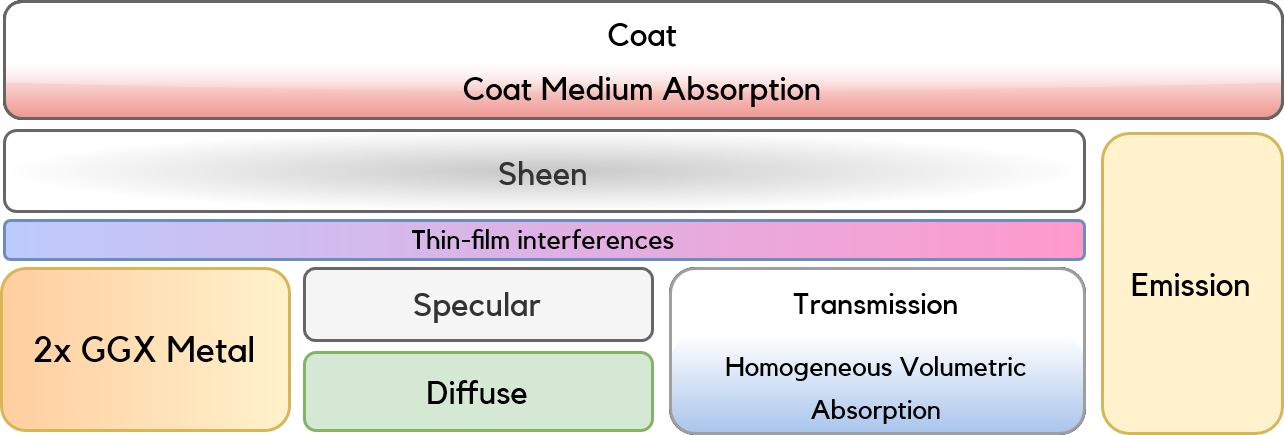
Layered Principled BSDF:
- Coat Microfacet GGX Layer + Anisotropy, Anisotropy Rotation, Medium Absorption & Thickness
- On-the-fly Monte Carlo integration for energy compensation of interlayer clearcoat multiple scattering
- SGGX Volumetric Sheen Lobe LTC Fit [Zeltner, Burley, Chiang, 2022]
- Specular Microfacet GGX Layer
- Oren-Nayar Diffuse BRDF Lobe
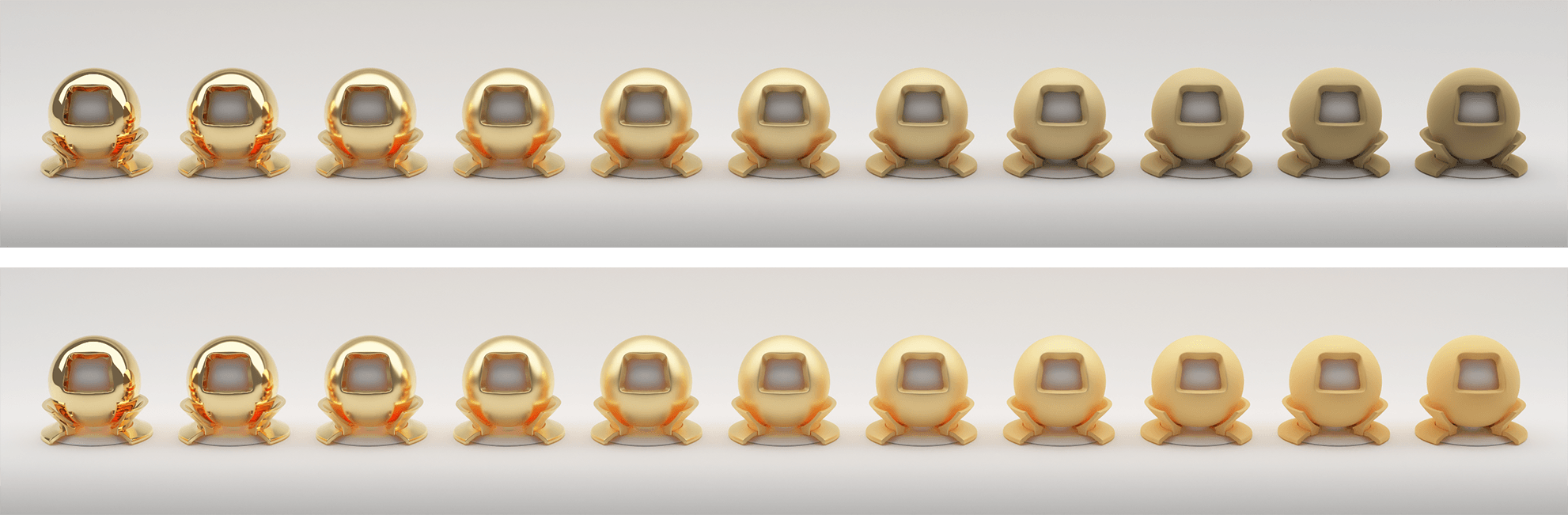
- Metallic Microfacet GGX Layer + Anisotropy & Anisotropy Rotation + Double Roughness [Kulla & Conty, 2017]
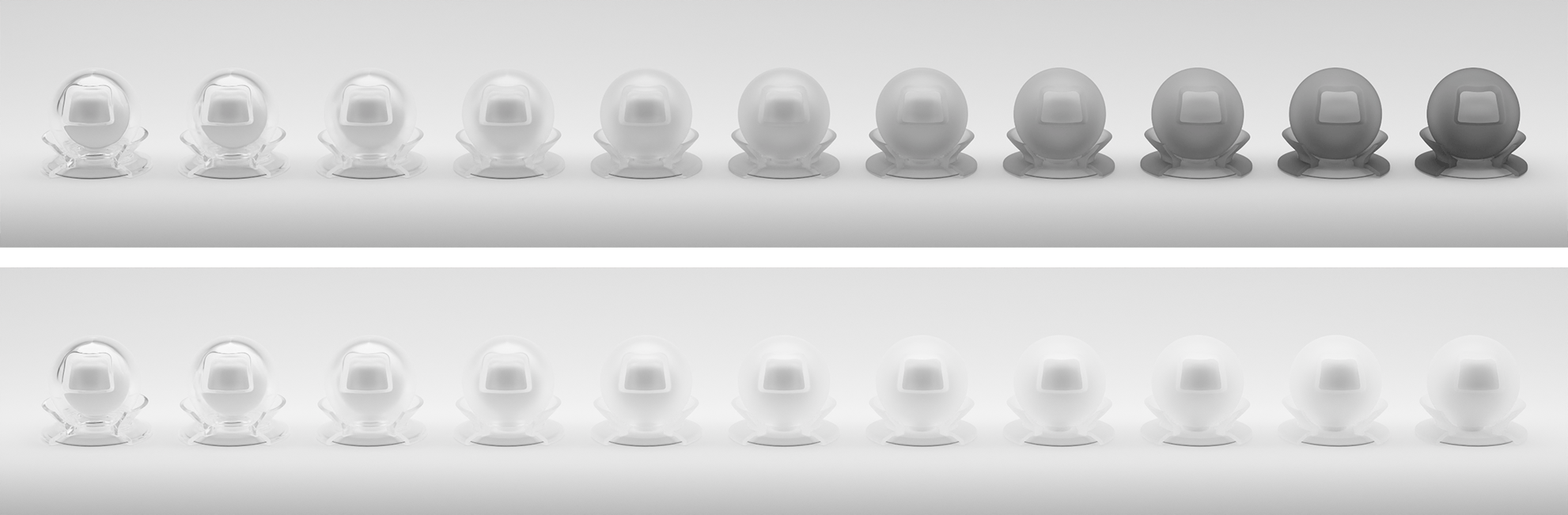
- Specular transmission BTDF + Beer Lambert Volumetric Absorption: [Burley, 2015]
- Diffuse lambertian BTDF
- Spectral dispersion using Cauchy’s equation
- Multiple-scattering energy compensation for conductors (double metal layer), dielectrics (transmission layer) and glossy-diffuse (specular + diffuse layer) materials [Turquin, 2019]
- Thin-film interference over dielectrics and conductors [Belcour, Barla, 2017]
- Thin-walled model
Sampling
- Base light sampling techniques:
- Uniform light sampling for direct lighting estimation + MIS
- Power-proportional light sampling
- ReGIR [Boksansky et al., 2021] augmented with:
- Representative cell surface-data + integration with NEE++ for resampling according to the product BRDF * L_i * G * V
- Visibility reuse
- Spatial reuse
- Hash grid
- Per-cell RIS integral normalization factor pre-integration for multiple importance sampling support \
- Next-event estimation strategies (built on-top of base techniques):
- MIS with BSDF sampling
- Resampled Importance Sampling (RIS) [Talbot et al., 2005]+ Weighted Reservoir Sampling (WRS) for many light sampling + [M. T. Chao, 1982]
- ReSTIR DI
- Next Event Estimation++ [Guo et al., 2020] + Custom envmap support
- HDR Environment map + Multiple Importance Sampling using
- CDF-inversion & binary search
- Alias Table (Vose’s O(N) construction [Vose, 1991])
- BSDF sampling:
- GGX NDF Sampling:
- Visible Normal Distribution Function (VNDF) [Heitz, 2018]
- Spherical caps VNDF Sampling [Dupuy, Benyoub, 2023]
- GGX NDF Sampling:
- Path sampling:
- BSDF Sampling:
- One sample MIS for lobe sampling [Hery et al., 2017]
- ReSTIR GI [Ouyang et al., 2021]
- Experimental warp-wide direction reuse for improved indirect rays coherency [Liu et al., 2023]
- BSDF Sampling:
- ReSTIR Samplers:
- ReSTIR DI [Bitterli et al., 2020]
- Supports envmap sampling
- Fused Spatiotemporal Reuse [Wyman, Panteleev, 2021]
- Light Presampling [Wyman, Panteleev, 2021]
- ReSTIR GI [Ouyang et al., 2021]
- Many bias correction weighting schemes:
- 1/M
- 1/Z
- MIS-like,
- Generalized balance heuristic
- Pairwise MIS [Bitterli, 2022] & defensive formulation [Lin et al., 2022])
- Pairwise symmetric & asymmetric ratio MIS weights [Pan et al., 2024]
- Adaptive-directional spatial reuse for improved offline rendering efficiency
- Optimal visibility sampling [Pan et al., 2024]
- ReSTIR DI [Bitterli et al., 2020]
Other rendering features
- Microfacet Model Regularization for Robust Light Transport [Jendersie et al., 2019]
- G-MoN - Adaptive median of means for unbiased firefly removal [Buisine et al., 2021]
- Texture support for all the parameters of the BSDF
- Texture alpha transparency support
- Stochastic material opacity support
- Normal mapping
- Nested dielectrics support
- Handling with priorities as proposed in [Simple Nested Dielectrics in Ray Traced Images, Schmidt, 2002]
- A Low-Distortion Map Between Triangle and Square [Heitz, 2019]
- Per-pixel variance based adaptive sampling
- Intel Open Image Denoise + Normals & Albedo AOV support
UI
- Interactive ImGui interface
- Asynchronous interface to guarantee smooth UI interactions even with heavy path tracing kernels
- Interactive first-person camera
- Different frame-buffer visualization (visualize the adaptive sampling heatmap, converged pixels, the denoiser normals / albedo, …)
Other features
- Use of the [ASSIMP] library to support many scene file formats.
- Multithreaded scene parsing/texture loading/shader compiling/BVH building/envmap processing/… for faster application startup times
- Background-asynchronous path tracing kernels pre-compilation
- Shader cache to avoid recompiling kernels unnecessarily
Gallery
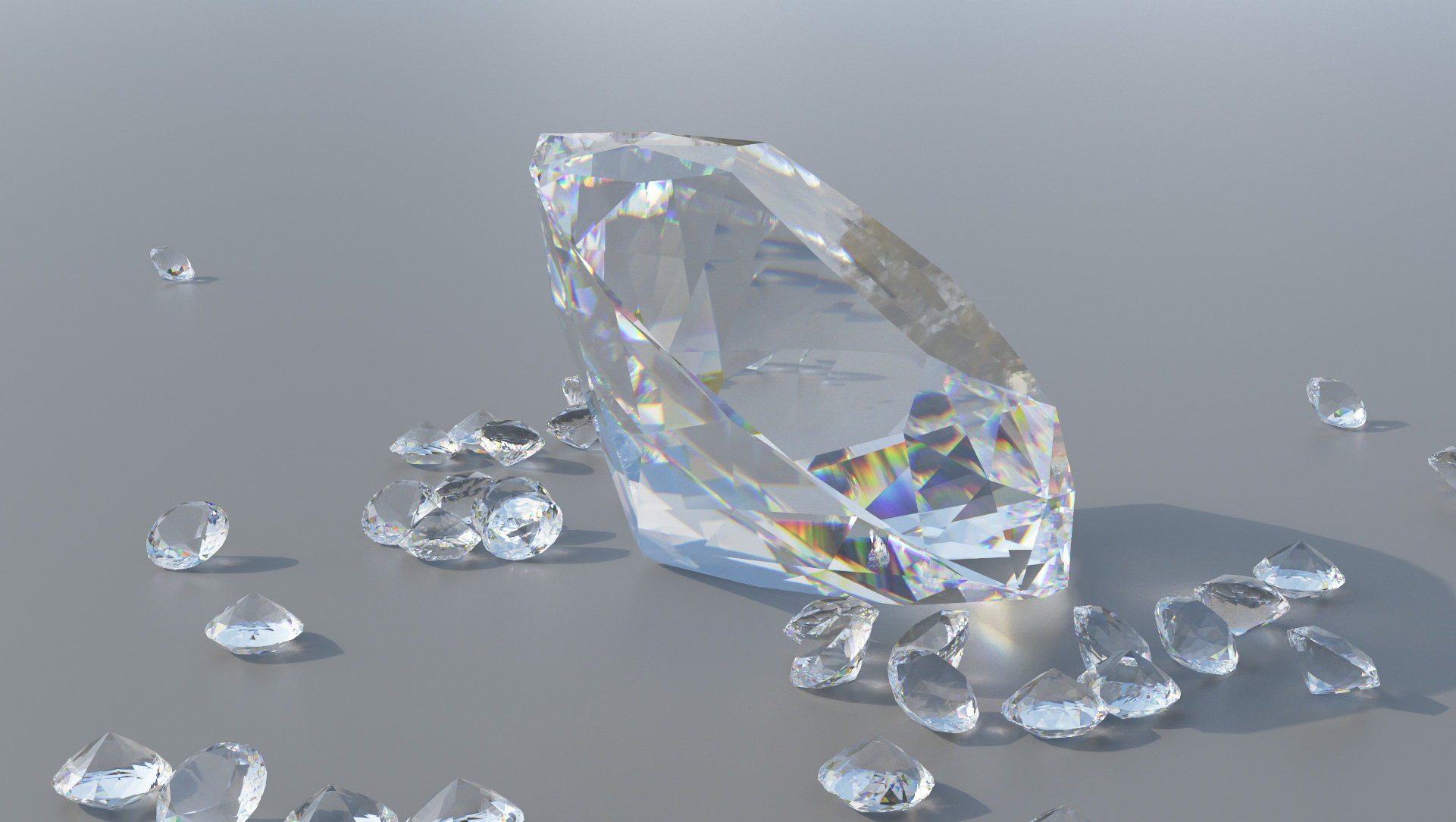
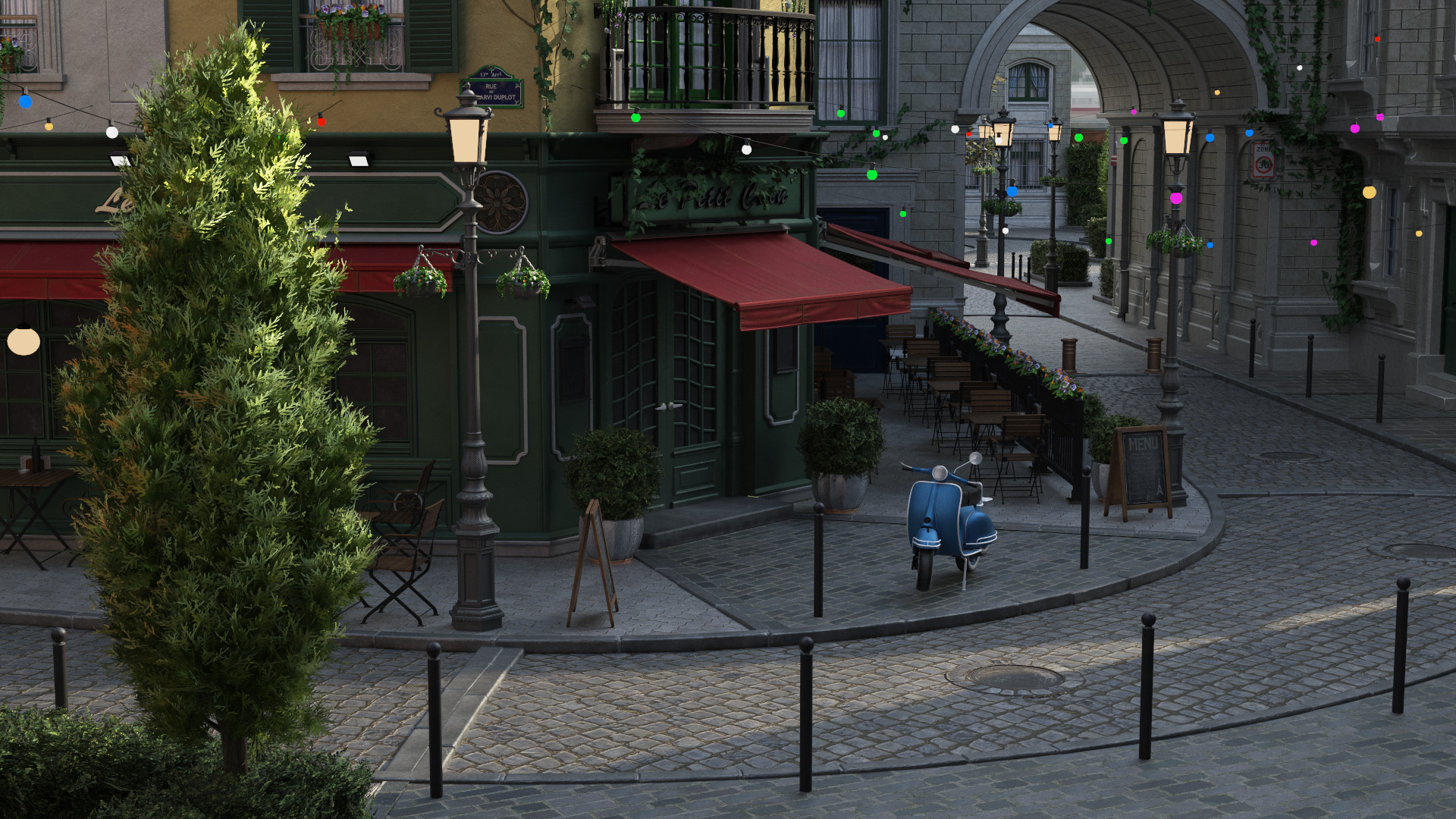
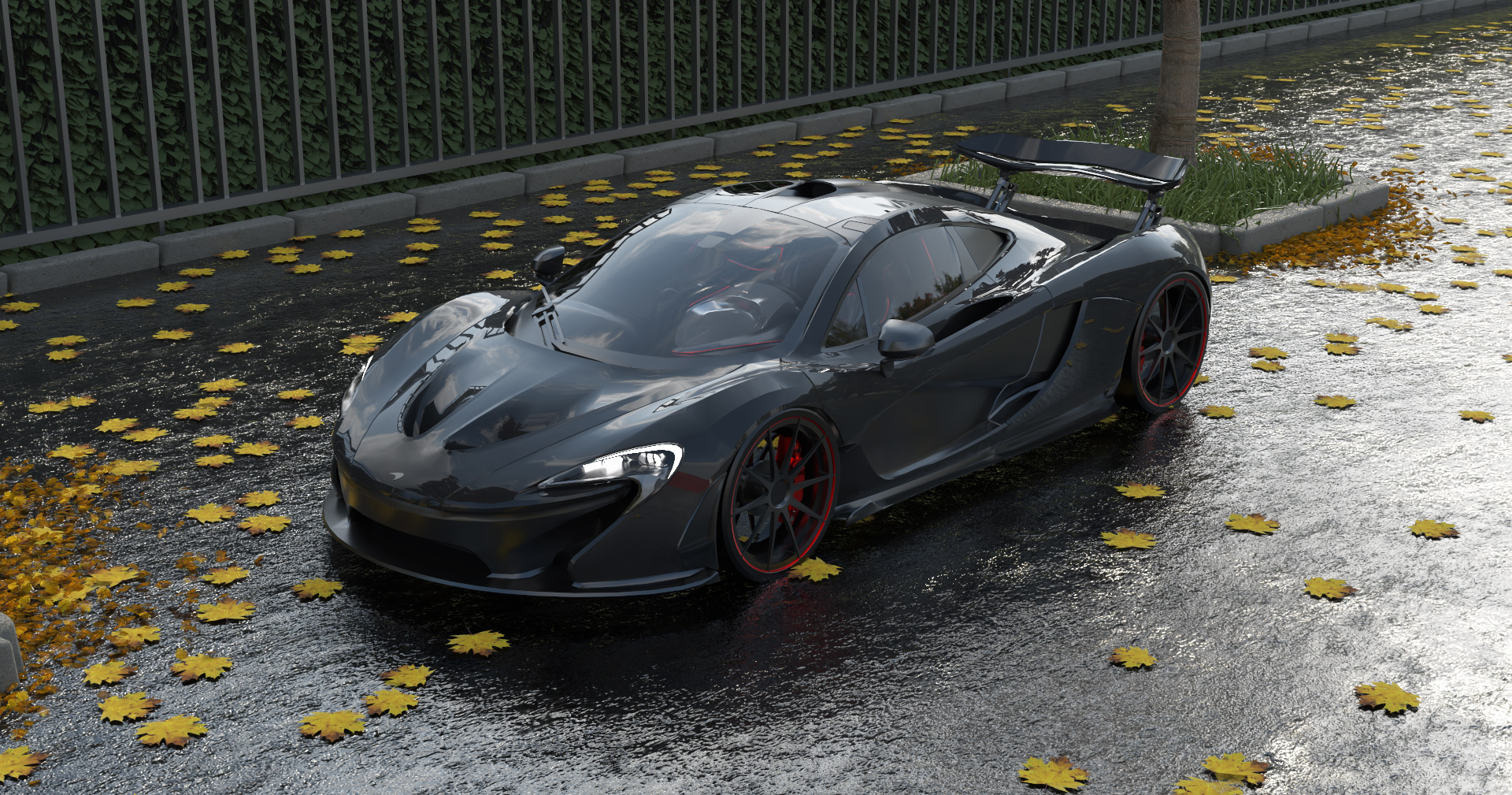
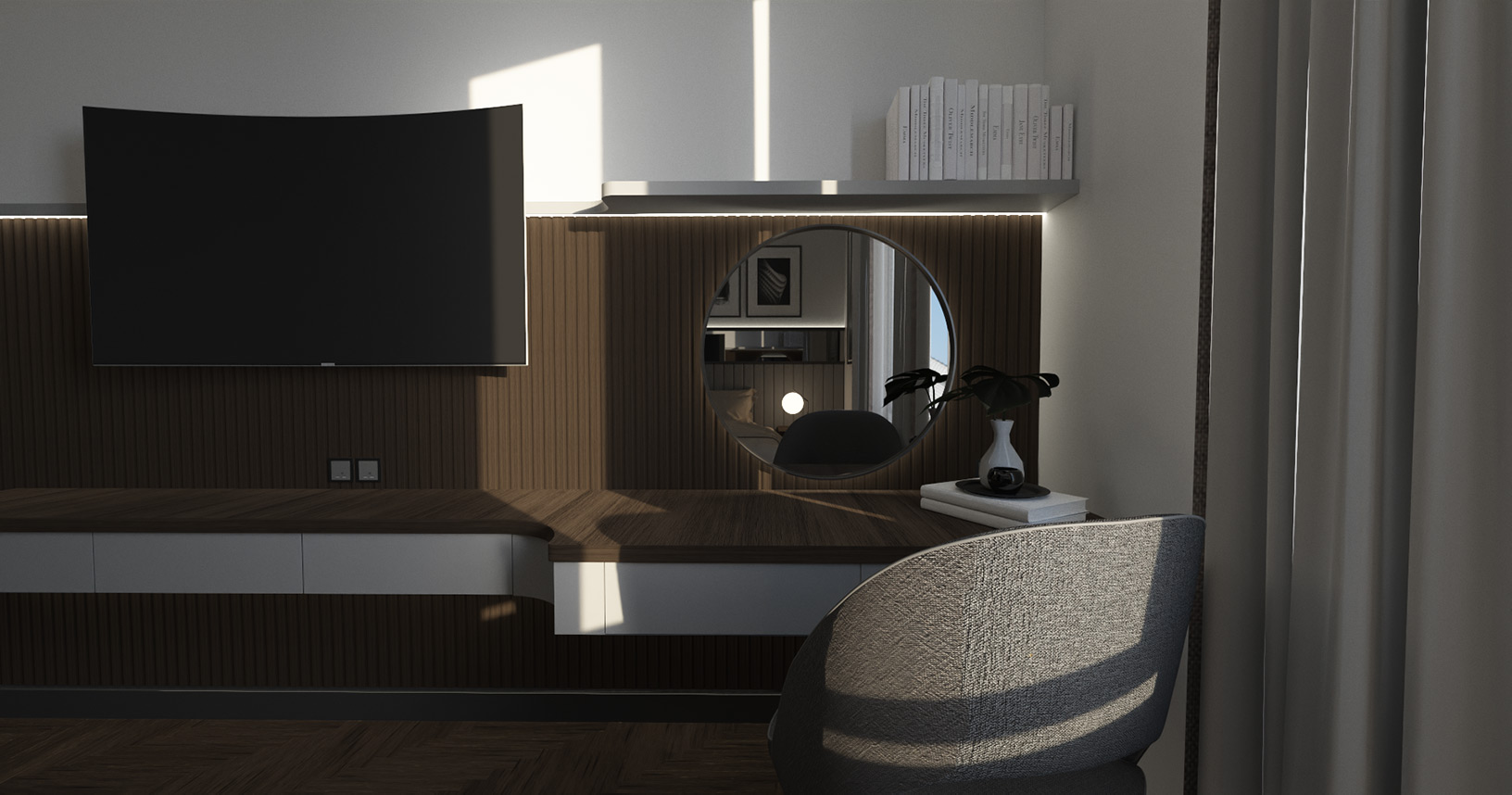
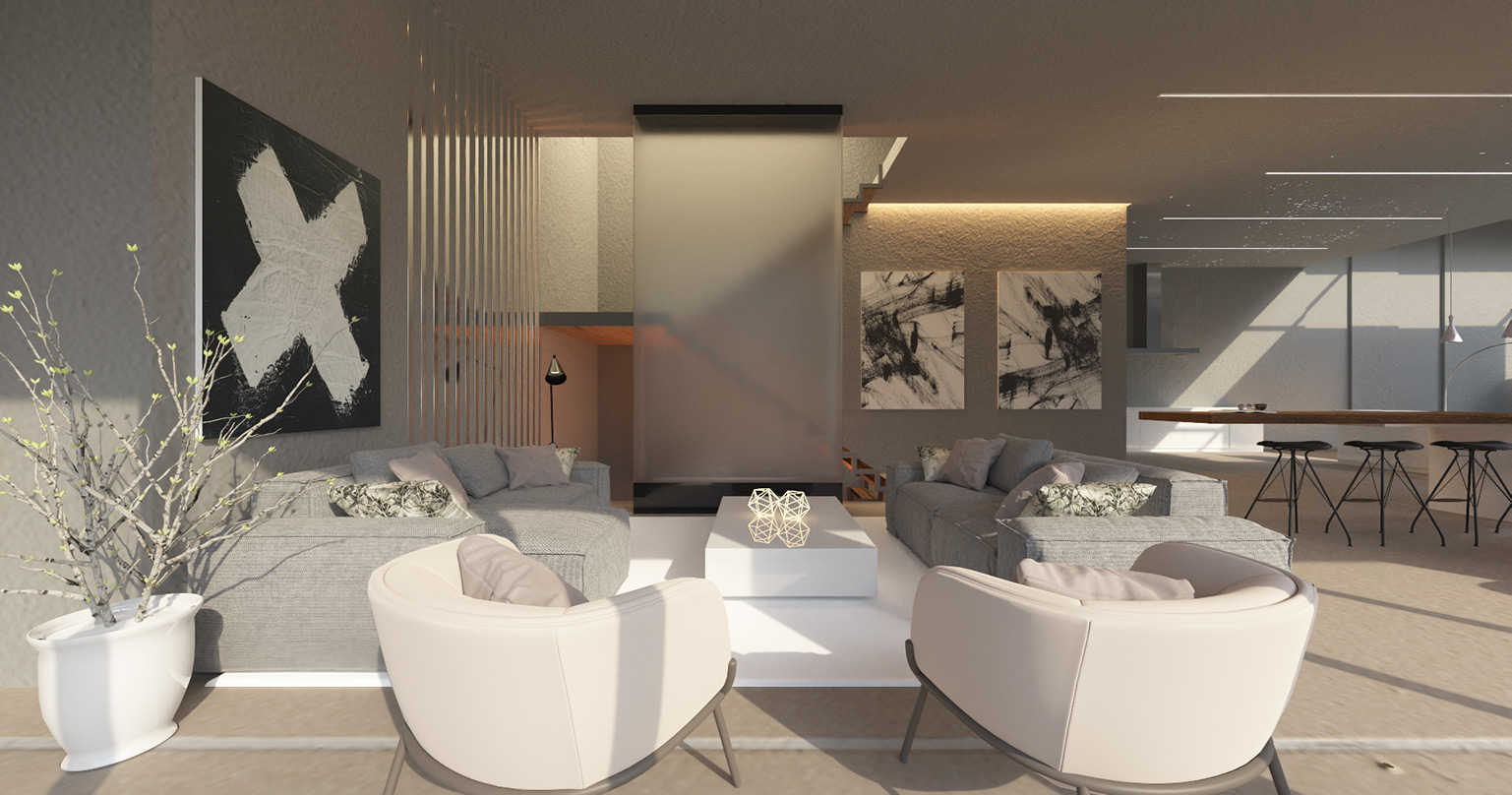
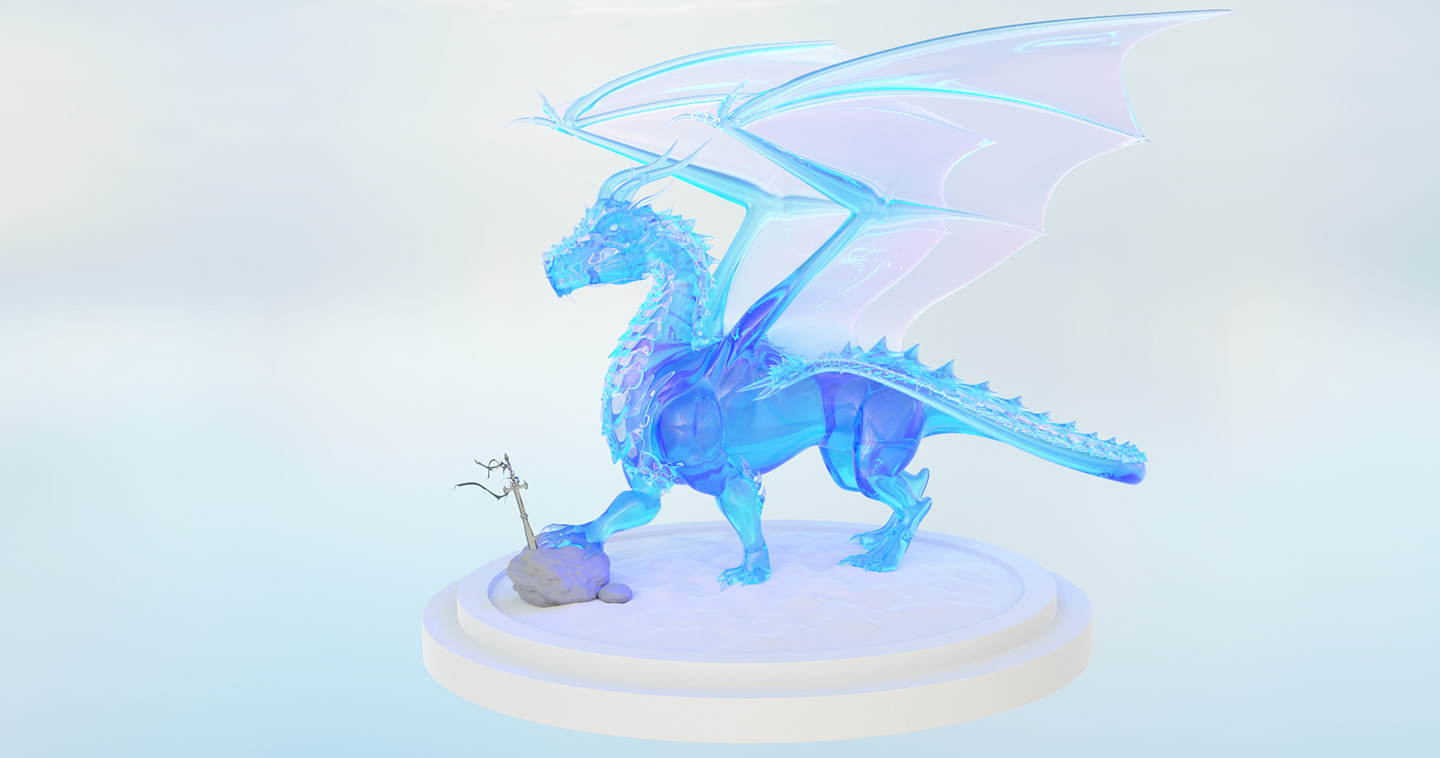
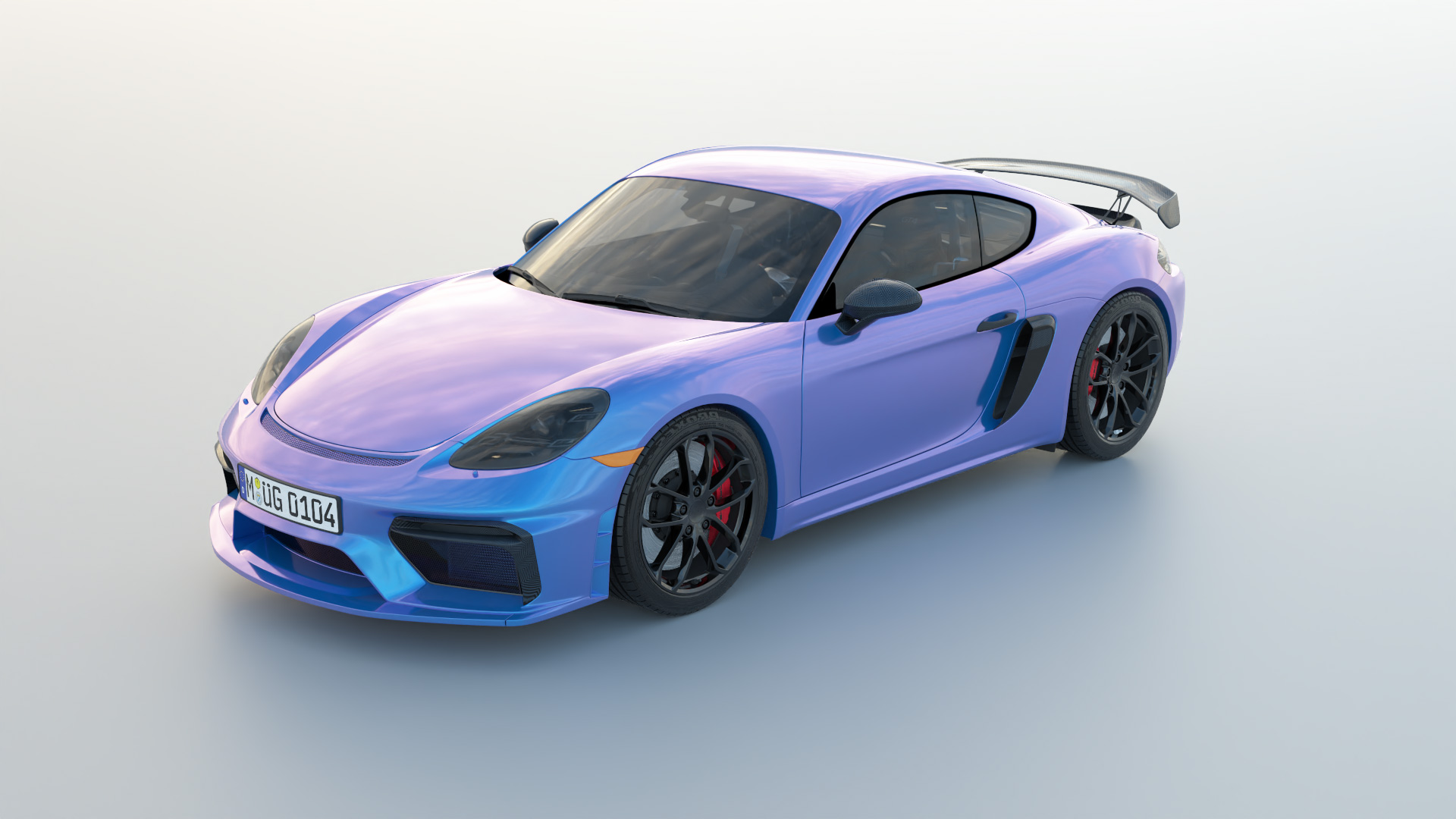
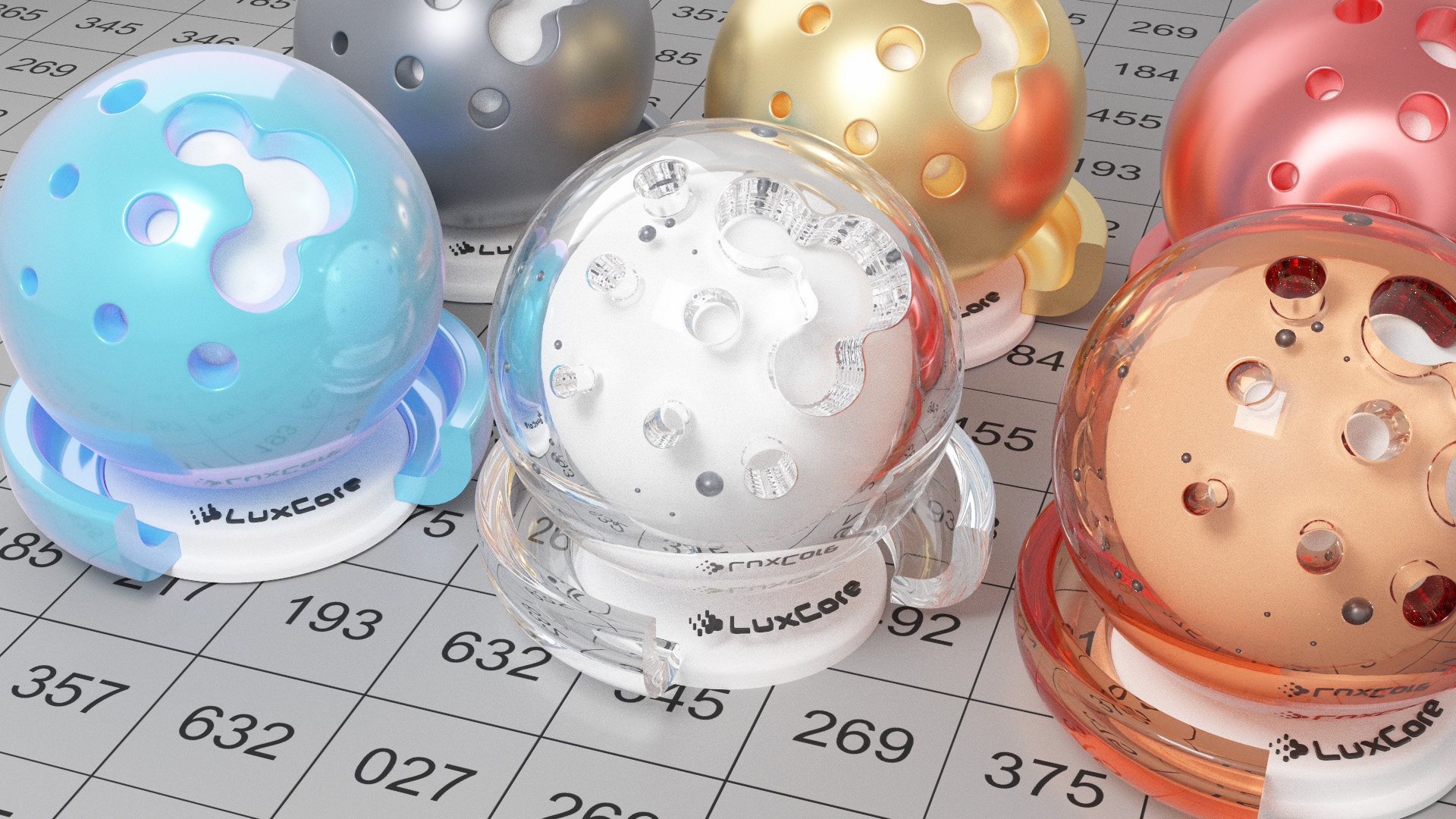
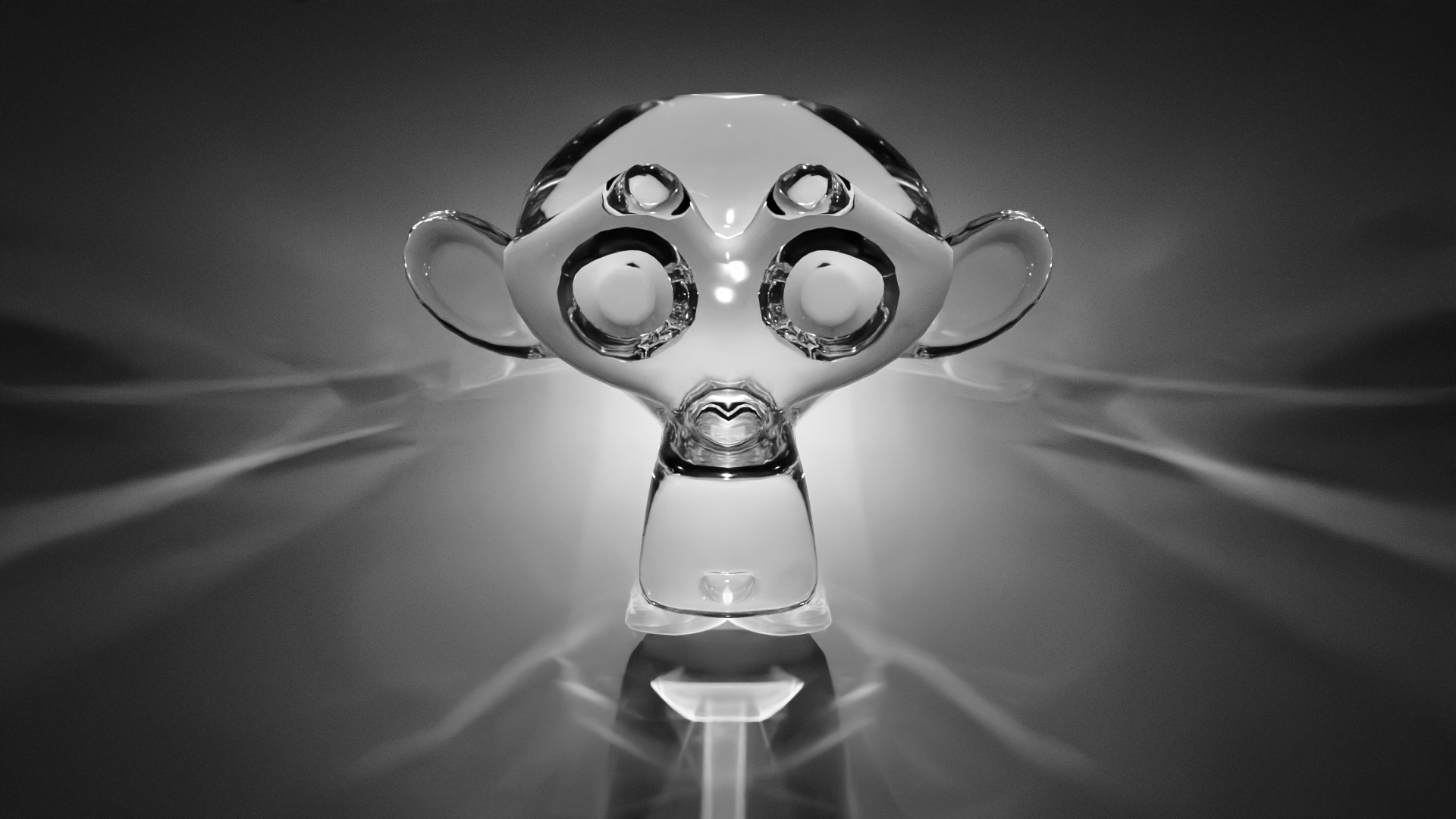









Live YouTube Showcases
Material Editor
OIDN AOVs Quality
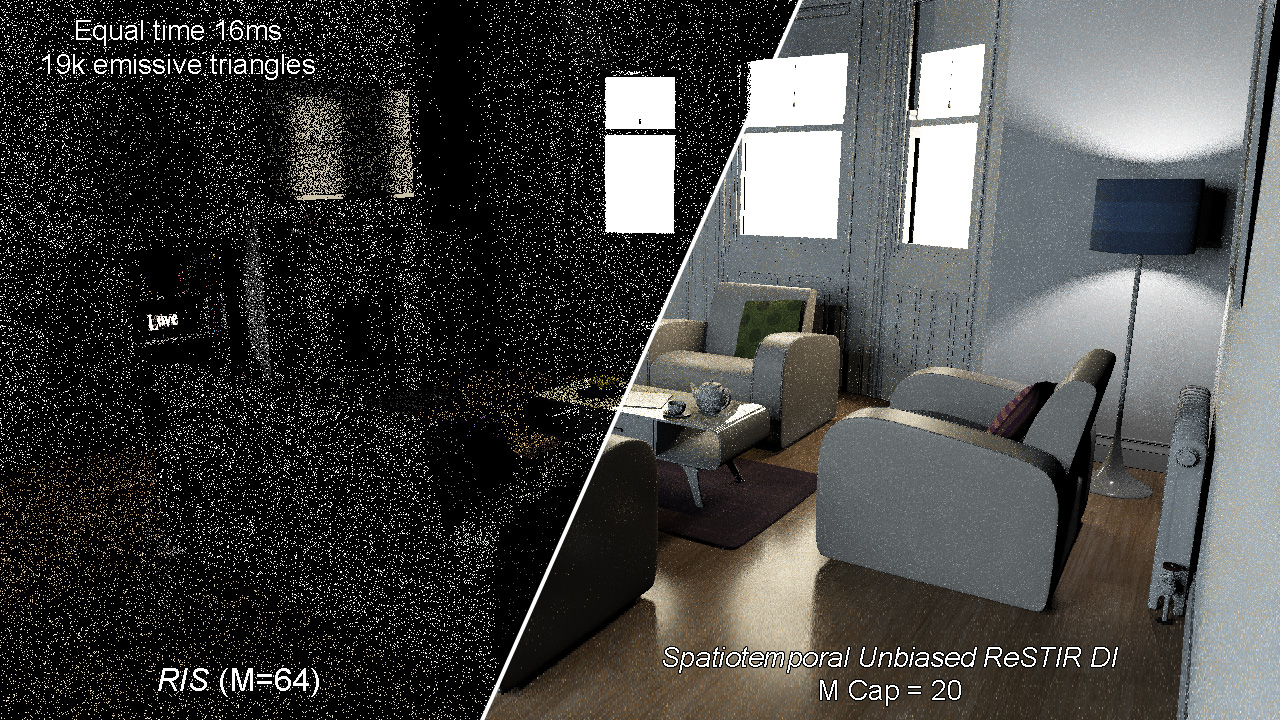
ReSTIR DI vs. RIS vs. MIS
Homogeneous Volumetric Absorption
ReSTIR DI & Dynamic Envmap
SGGX Volumetric Sheen Lobe LTC Fit
Conductors/Dielectrics Multiple Scattering Energy Compensation
Thin-film Iridescence Render [Belcour, Barla, 2017]
Spectral dispersion in glass
Related Blog Posts
Github
This project is open-source on Github: HIPRT-Path-Tracer